Covid 19 Antibiotic Guidance - Covid-19 Realtime Info
The covid 19 pandemic and antimicrobial resistance are parallel and interacting health emergencies with opportunity for mutual learning.
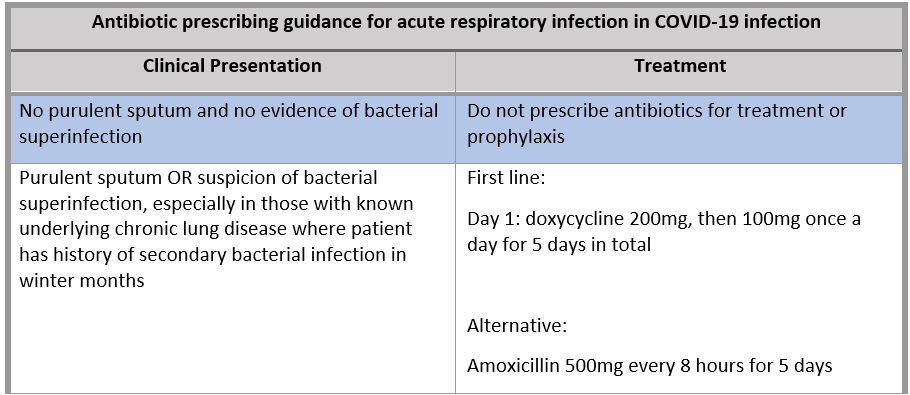
Covid 19 antibiotic guidance. 3 the guidance further states that empiric antibiotic bacterial pneumonia treatment can be. As their measures and consequences are comparable the covid 19 pandemic helps to illustrate the potential long term impact of amr which is less acute but not less crucial. The guidelines for the diagnosis treatment and control of the coronavirus disease 2019 covid 19. Coronavirus covid 19 were supporting the nhs and social care by providing guidance about covid 19 and backing efforts to get promising diagnostics and treatments to patients quickly.
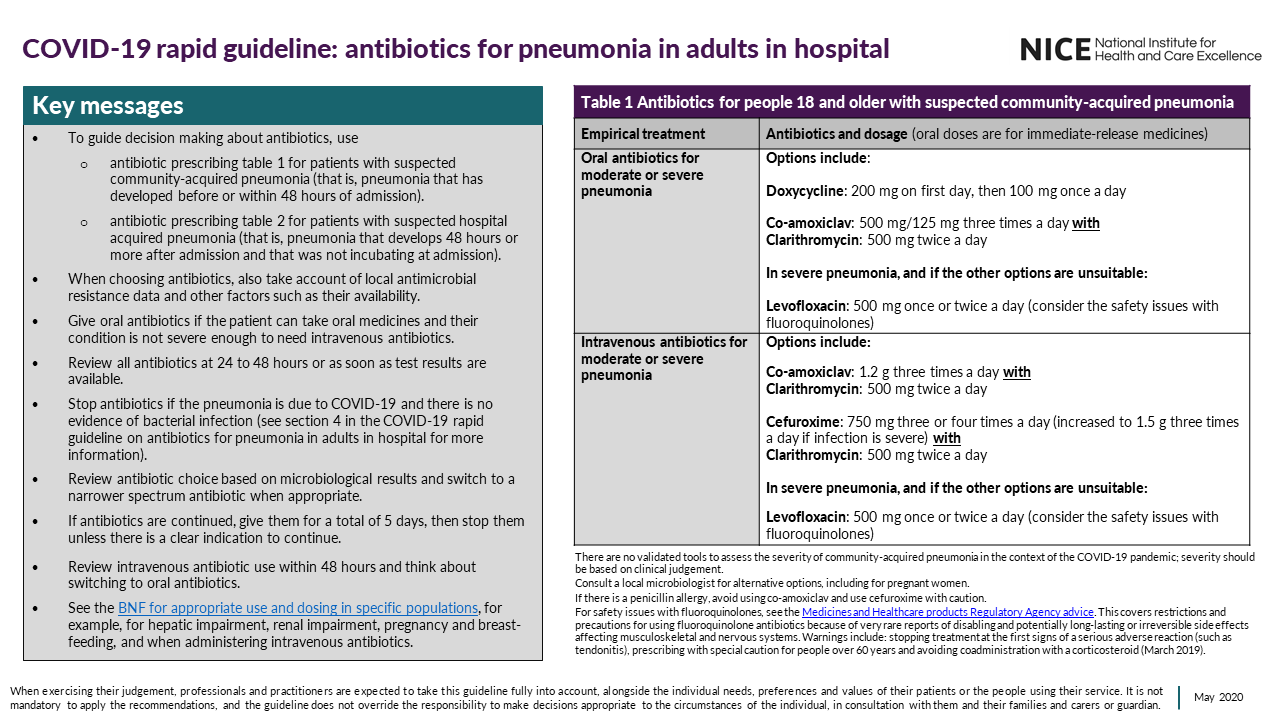
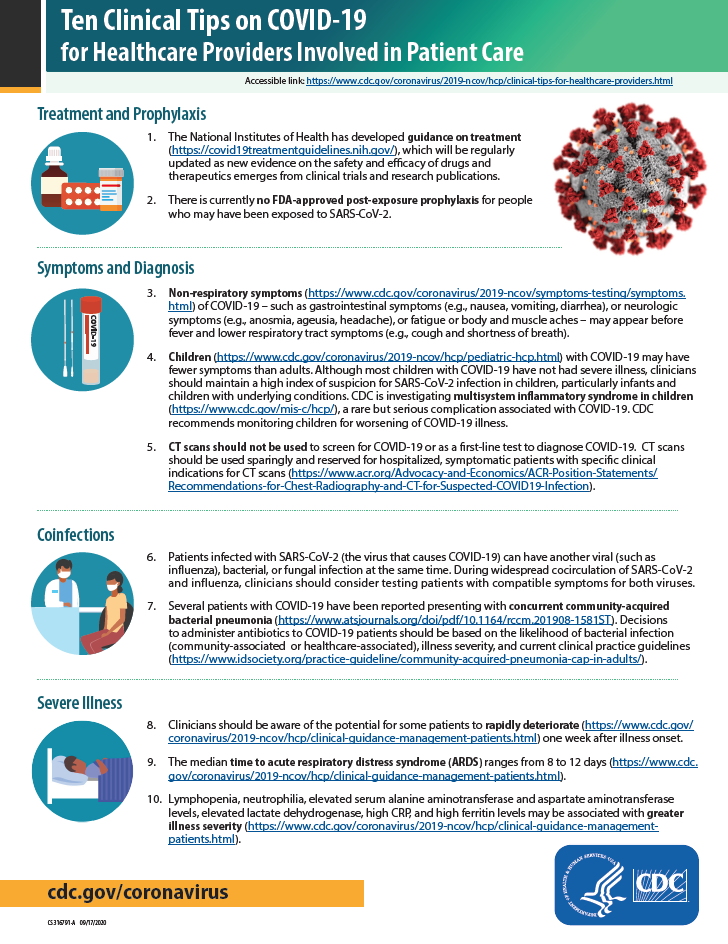
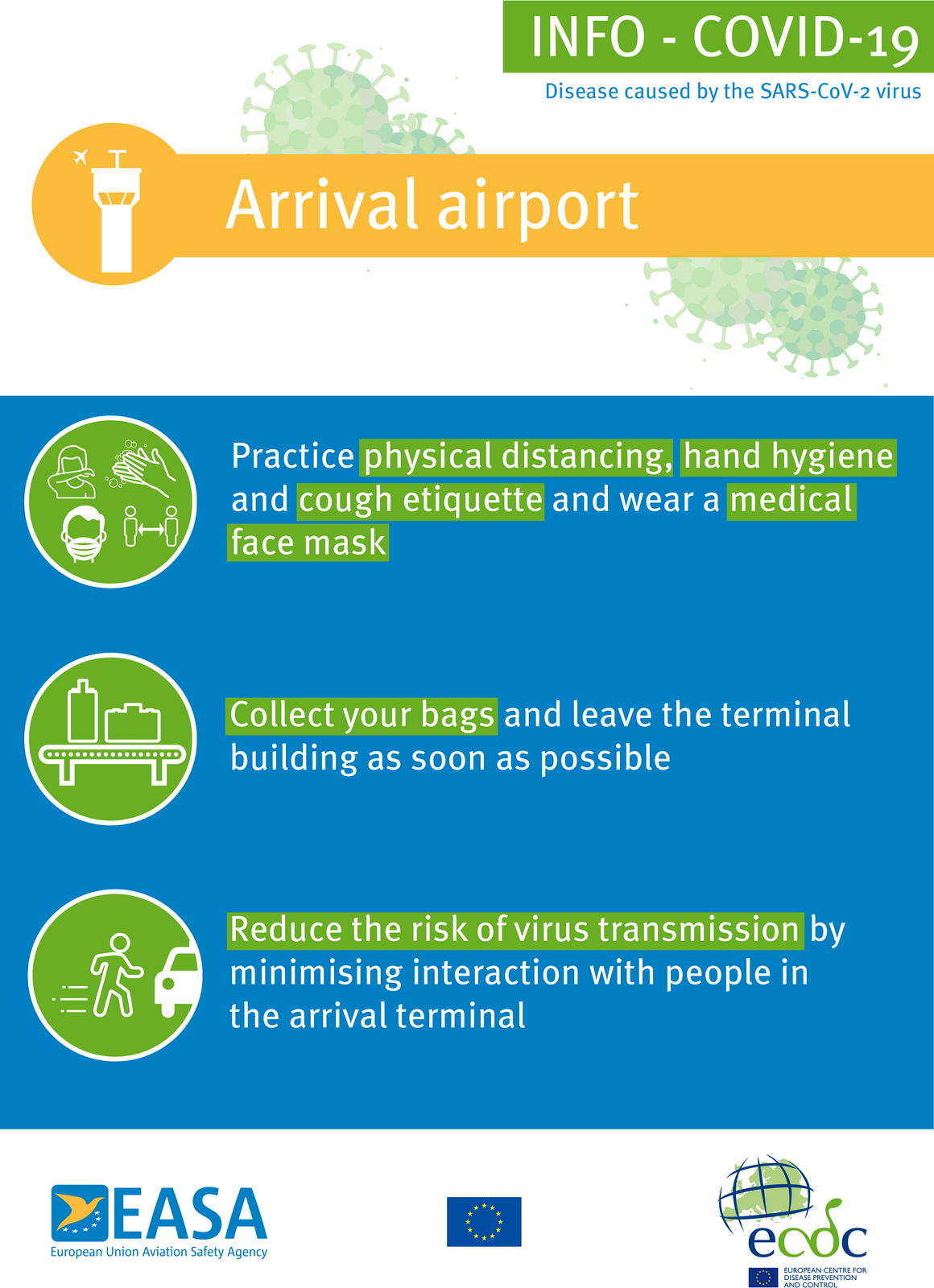
For general advice on managing covid 19 symptoms see the nice covid 19 rapid guideline on managing symptoms including at the end of life in the community. Inappropriate antibiotic use may reduce availability if used indiscriminately and broad spectrum antibiotics in particular may lead to clostridioides difficile infection and antimicrobial resistance. We update our guidance when new evidence comes out so that the health and care system can find current reliable advice as it continues to respond to the. On 23 april 2020 we clarified the recommendations on antibiotic treatment for bacterial pneumonia in the community during the covid 19 pandemic.
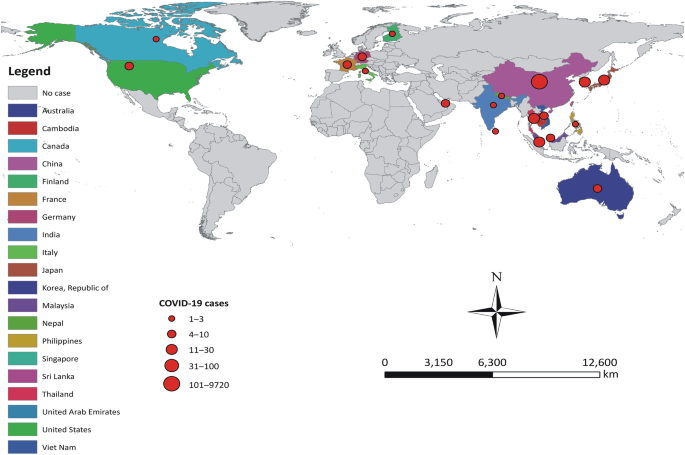
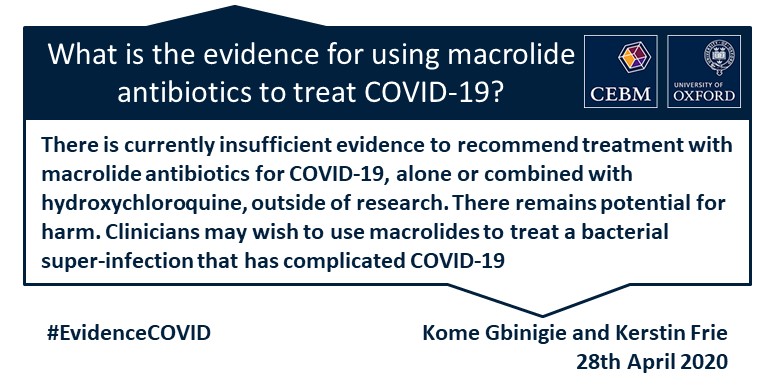
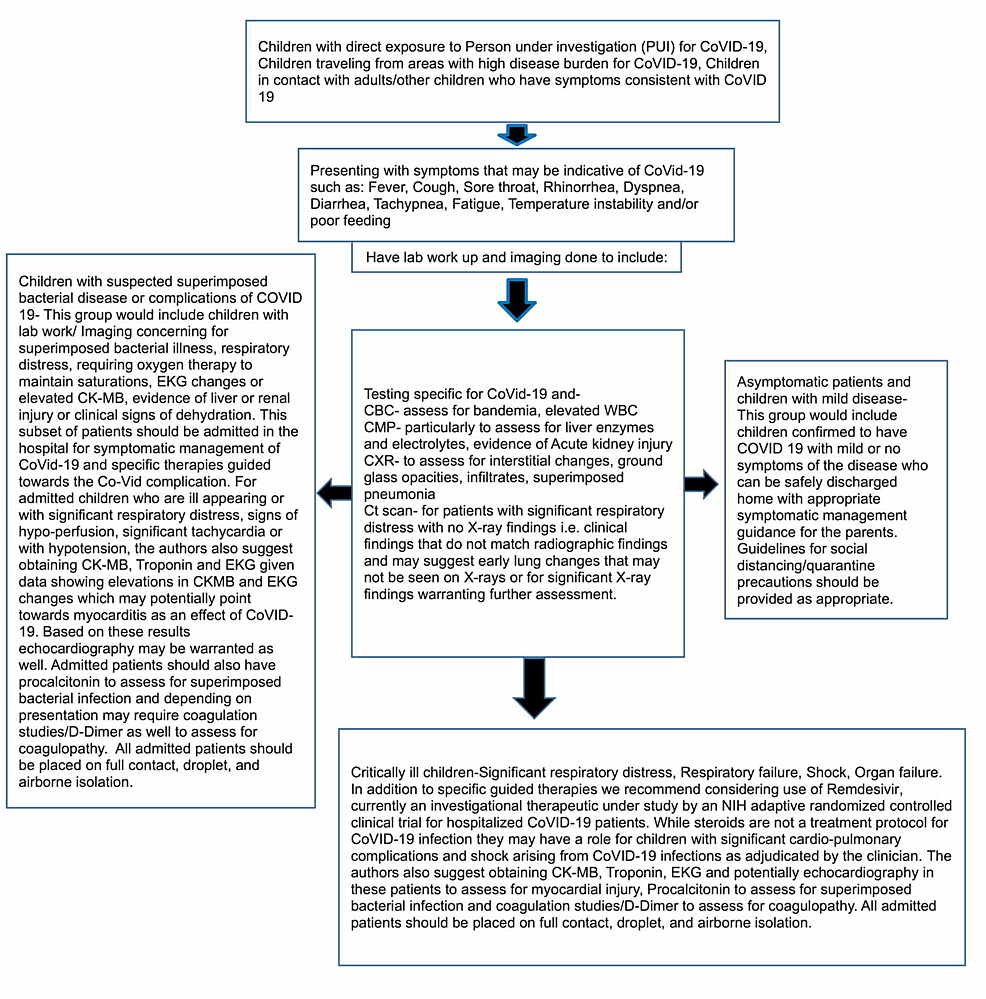
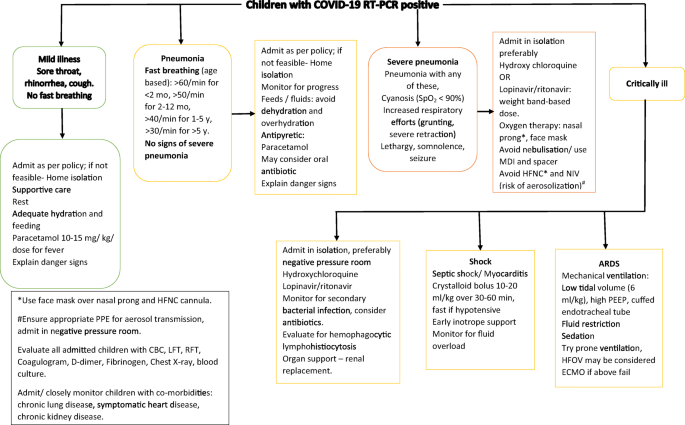
The use of empiric antibiotic treatment for patients with suspected or confirmed severe covid 19 based on clinical judgement considering patient host factors and local epidemiology along with daily assessments for de escalation is recommended. Reports thus far have not identified unusual associations between covid 19 infection and bacterial co infection. Evidence so far suggests that bacterial co infection occurs in less than about 10 of patients with covid 19. Access cdcs guidance documents for coronavirus disease 2019 covid 19 sorted by audience.
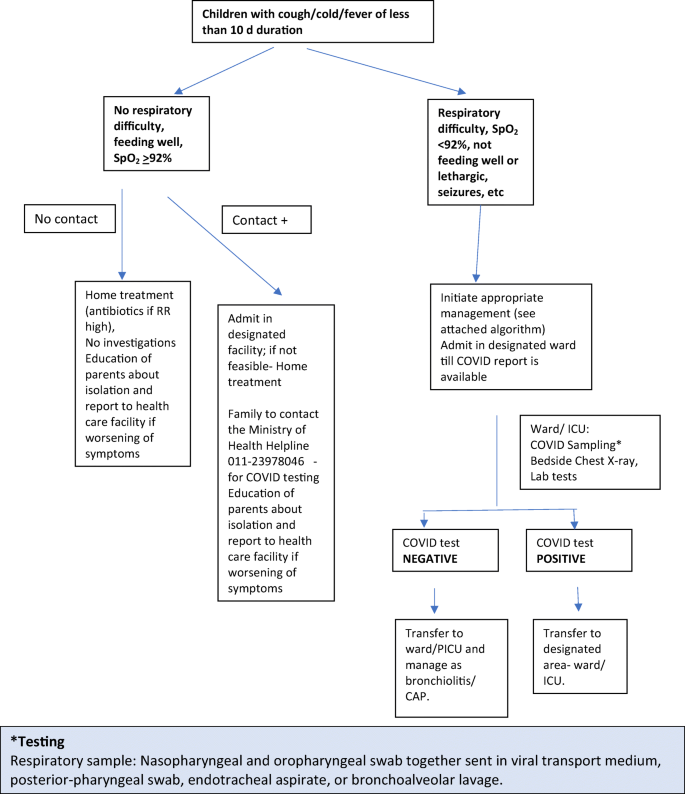
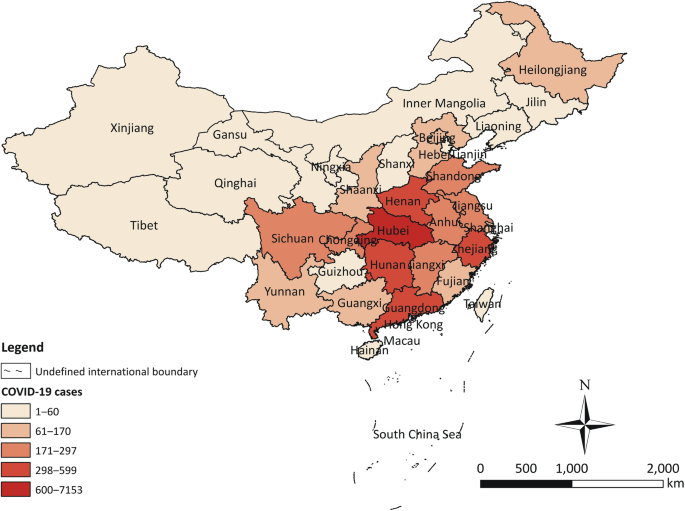
In patients who test negative for covid 19 pneumonia antibiotic therapy should be based on guidance provided in the institutional pneumonia treatment and procalcitonin usage guidelines. This includes people presenting to hospital with moderate to severe community acquired pneumonia and people who develop pneumonia while in hospital. Coronavirus disease 2019 covid 19 is a virus more specifically a coronavirus identified as the cause of an outbreak of respiratory illness first detected in wuhan china. Between covid 19 pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia on clinical features alone see recommendations 42 and 43.
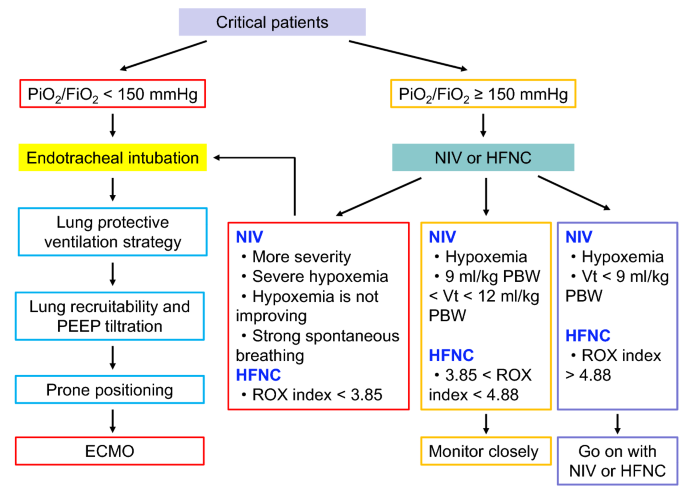
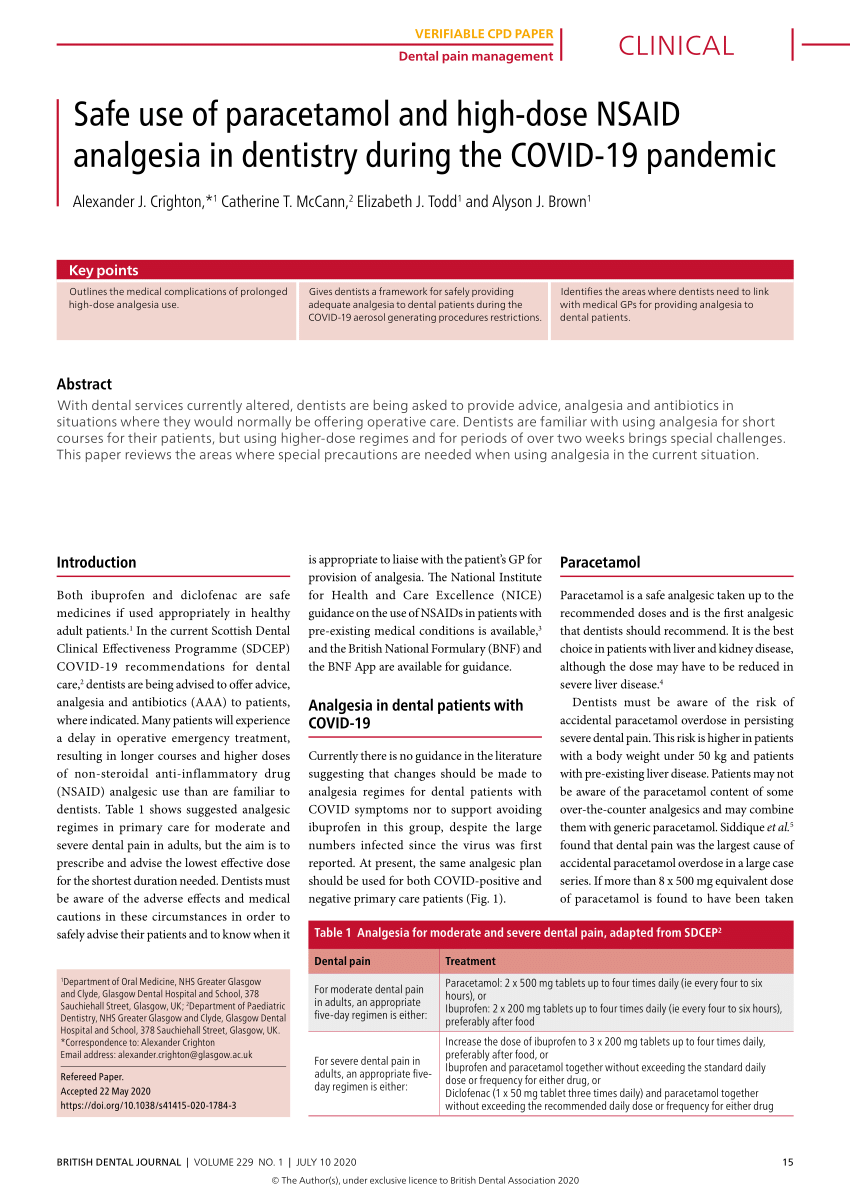
The purpose of this guideline is to ensure the best antibiotic management of suspected or confirmed bacterial pneumonia in adults in hospital during the covid19 pandemic.